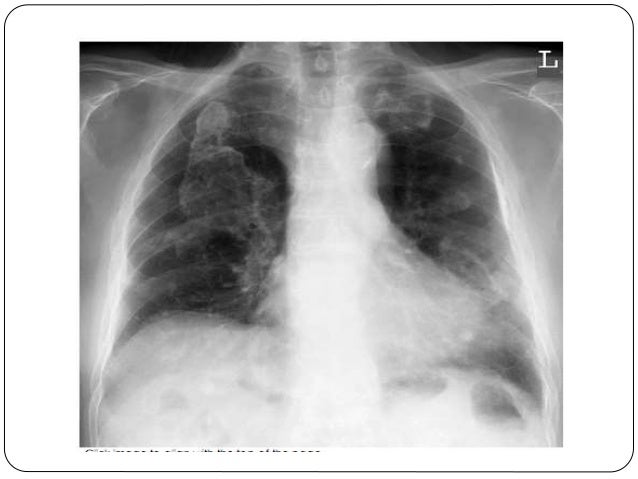
Pleural Thickening Radiology Ct, Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging
Pleural thickening radiology ct Indeed lately is being hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. Individuals now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of the article I will discuss about Pleural Thickening Radiology Ct.
- Thorax 8 2 Pleural Space Case 8 2 2 Benign And Malignant Pleural Thickening Ultrasound Cases
- Benign Pleural Thickening Radiology Key
- Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging
- Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging
- Apical Pleural Thickening On Chest X Ray
- Initial Chest X Ray And Ct Show That Massive Pleural Ef Open I
Find, Read, And Discover Pleural Thickening Radiology Ct, Such Us:
- Malignant Mesothelioma Radiographics
- 28 Radiology Key
- Comparative Interpretation Of Ct And Standard Radiography Of The Pleura
- Pleural Tuberculosis A Key Differential Diagnosis For Pleural Thickening Even Without Obvious Risk Factors For Tuberculosis In A Low Incidence Setting Bmj Case Reports
- Investigation Of A Unilateral Pleural Effusion In Adults British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline 2010 Thorax
- Free Printable Female Superhero Coloring Pages
- Commercial Real Estate Attorney
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma Chemotherapy
- Mesothelioma Spots On Lungs
- Irregular Pleural Thickening
If you re looking for Irregular Pleural Thickening you've arrived at the right location. We have 104 images about irregular pleural thickening including pictures, photos, photographs, backgrounds, and more. In such page, we also provide number of images available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, translucent, etc.
Chronic ischemic etiology is favored for most cases 4.
Irregular pleural thickening. It arises from a number of causes. Diffuse pleural thickening refers to a morphological type of pleural thickening. Typically seen a continuous sheet of pleural thickening often involving the costophrenic angles and apices without calcification 2 3.
Diffuse pleural fibrosis fibrothorax 6. The authors present a review of basic pleural anatomy and imaging features of both benign and malignant pleural neoplasms. Microscopically they are composed of dense hyalinised collagen and are relatively acellular.
Plaques typically have edges that are thicker than the central portion fig. Our investigation of 28727 chest x rays obtained from annual health examinations confirmed that pleural thickening was the most common abnormal radiological finding. It can occur with both benign and malignant pleural disease.
Ct is particularly useful in defining the location and extent of these masses. Although pleural thickening is a common finding on routine chest x rays its radiological and clinical features remain poorly characterized. Pleural thickening is a descriptive term given to describe any form of thickening involving either the parietal or visceral pleura.
Apical pleural cap refers to a curved density at the lung apex seen on chest radiograph. The frequency of apical pleural thickening increases with age 3. The specificity of this finding in diagnosing the presence of an exudate is 96.
The pleural may be involved by one of several primary or metastatic tumors. Functional consequences of pleural disease evaluated with chest radiography and ct. 738 and can progress in size extent and calcification with time.
In cases where multiple nodular regions or pleural thickening are present the diagnosis may be evident especially if a primary tumor or other metastatic deposits are visible. According to etiology it may be classified as. The portal venous phase also known as the pleural phase in the chest is.
Asbestos related pleural disease. It can occur from malignant as well as nonmalignant causes which include. Macroscopically pleural plaques appear as grey white regions of pleural thickening often thickest at the margins giving rise to the holly leaf appearance aside from the color of course.
Ct is the work horse of pleural imaging able to achieve specificities of close to 100 3. A pleural exudate in the absence of pleural thickening occurs most frequently in patients with malignancy or uncomplicated parapneumonic effusion. Axial ct image shows lobulated pleural thickening 1 cm double headed black arrow that also involves the mediastinal pleura white arrow.
In most cases 922 pleural thickening involved the apex of the lung particularly on.
More From Irregular Pleural Thickening
- Luigi Pumpkin Carving Template
- Environmental Asbestos Exposure And Mesothelioma
- Mesothelioma Settlements 2014
- Cool Fortnite Coloring Pages
- Chibi Coloring Book
Incoming Search Terms:
- Benign Pleural Thickening Radiology Key Chibi Coloring Book,
- Https Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Jmri 22372 Chibi Coloring Book,
- Treating Pleural Thickening Pleural Thickening Chibi Coloring Book,
- Investigating Pleural Thickening The Bmj Chibi Coloring Book,
- Ct Features Of Covid 19 Patients With Two Consecutive Negative Rt Pcr Tests After Treatment Scientific Reports Chibi Coloring Book,
- 2 Chibi Coloring Book,