Reactive Mesothelial Cells In Pleural Fluid Causes, Reliability Of P 16 Calretinin And Claudin 4 Immunocytochemistry In Diagnostic Verification Of Effusion Cytology
Reactive mesothelial cells in pleural fluid causes Indeed recently is being hunted by consumers around us, maybe one of you. Individuals are now accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the title of the post I will talk about about Reactive Mesothelial Cells In Pleural Fluid Causes.
- Pleural And Abdominal Fluid Cytology Vetfolio
- Malignant And Borderline Mesothelial Tumors Of The Pleura Thoracic Key
- Pb Reactive Mesothelial Hyperplasia Mimicking Mesothelioma In An African Green Monkey Chlorocebus Aethiops
- A Cytology Slide Demonstrating Numerous Mesothelial Cells In The Download Scientific Diagram
- Cytology Of Pleural And Peritoneal Lesions Chapter 5 Practical Pathology Of Serous Membranes
- Malignant Pleural Effusion From Bench To Bedside European Respiratory Society
Find, Read, And Discover Reactive Mesothelial Cells In Pleural Fluid Causes, Such Us:
- Reactive Mesothelial Hyperplasia Springerlink
- Jcdr Adenocarcinoma Immunocytochemistry Reactive Mesothelial Cells Serous Effusions
- Serous Effusions Basicmedical Key
- Effusions Mspca Angell
- Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key
- Halloween Adventure
- Cheshire Cat Pumpkin Carving Ideas
- Free Pixel Color By Number
- Pickup Truck Coloring Pages
- Carson Lawrence
If you are looking for Carson Lawrence you've reached the perfect place. We ve got 104 graphics about carson lawrence adding images, pictures, photos, backgrounds, and much more. In such webpage, we additionally have number of graphics out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, logo, black and white, transparent, etc.

Cytologic Differential Diagnosis Among Reactive Mesothelial Cells Malignant Mesothelioma And Adenocarcinoma Kitazume 2000 Cancer Cytopathology Wiley Online Library Carson Lawrence
Reactive mesothelial cells tend to come in.
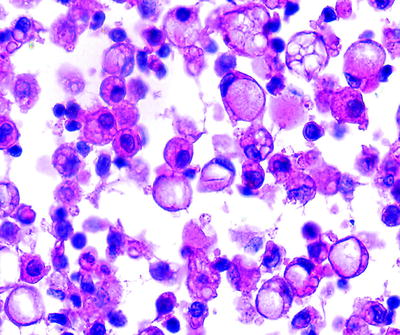
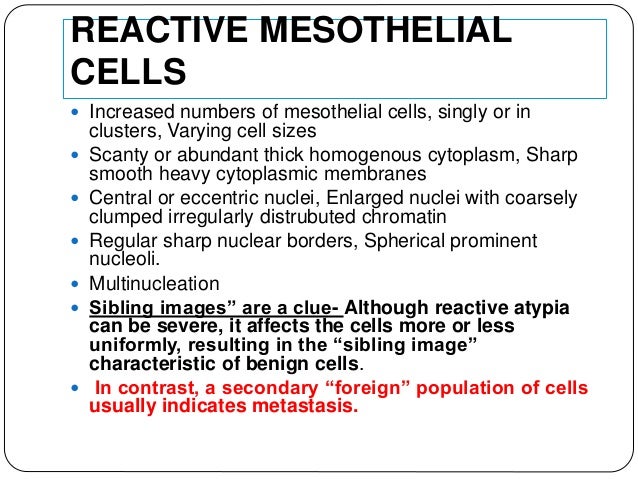
Carson lawrence. The pleural mesothelium differentiates to give rise to the endothelium and smooth muscle cells via epithelial to mesenchymal transition emt. Although mesothelial cells have a distinctive morphology reactive mesothelial cells may display atypical appearances that can be interpreted as malignancy. Metastatic adenocarcinoma is the most common malignancy diagnosed on effusions.
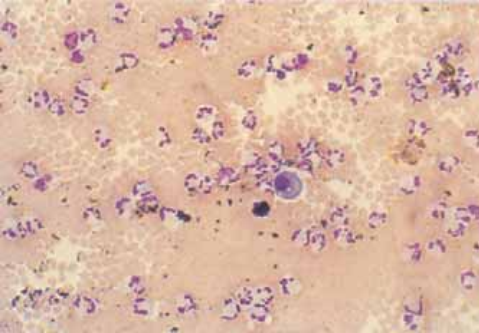
It can also be the result of trauma or the presence of metastatic tumor. Pleural mesothelial cells pmcs derived from the mesoderm play a key role during the development of the lung. Numerous mesothelial cells are seen in this pleural fluid from a dog with a transudative effusion with concurrent diapedesis of red blood cells or hemorrhage.
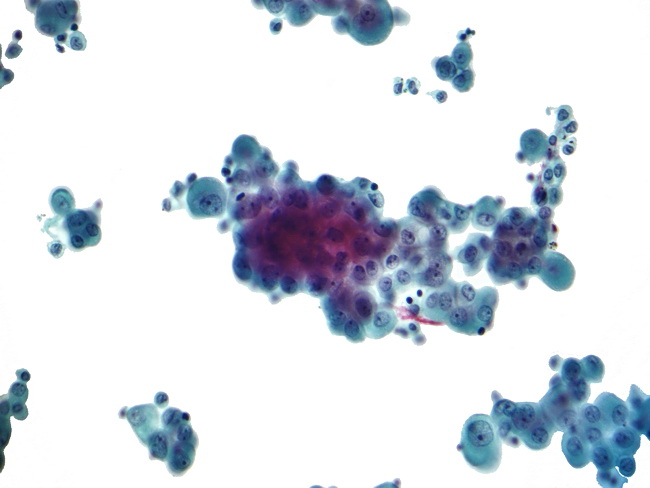
During development the mesoderm maintains a complex relationship with the developing endoderm giving rise to the mature lung. Reactive mesothelial cells can be found when there is an infection or an inflammatory response present in a body cavity. Mesothelial hyperplasia is often accompanied by pleural fibrosis figure 2324 in cases of subpleural inflammation and especially when inflammation is chronic active and may occur as micropapillary fronds of mature connective tissue covered by a single layer of flattened to cuboidal mesothelial cells figure 2325.
One of the characteristic cytomorphologic features of adenocarcinoma is the presence of intracytoplasmic. This condition can be caused by the presence of bacterial viral or fungal. This condition can be due to the presence of a bacterial viral or fungal infection.
The mesothelial cells have central round nuclei with a moderate amount of light purple cytoplasm and a corona or fringe to the cytoplasmic borders. It can also be the result of trauma or the presence of metastatic cancer.
More From Carson Lawrence
- Halloween Coloring Sheets Pdf
- Halloween Hump Day Pictures
- Mesothelioma Attorney Colorado
- Simmons Beautyrest Greenmont Plush
- Mesothelioma Blood Pressure
Incoming Search Terms:
- Malignant And Borderline Mesothelial Tumors Of The Pleura Thoracic Key Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,
- Mesothelium Wikipedia Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,
- Pleural Effusions In Lung Cancer Detection And Treatment Intechopen Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,
- Serous Effusions Basicmedical Key Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcsz17zwtswsxrxukidpxvwfogfg Lmw2zu2hrwffdak6gxn1 Lh Usqp Cau Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,
- Http Www Api Pt Com Reference Commentary 2015ascope Pdf Mesothelioma Blood Pressure,