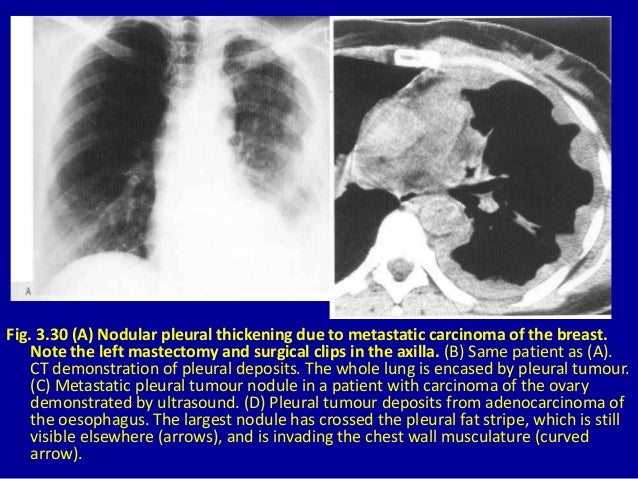
Nodular Pleural Thickening Radiology, Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging
Nodular pleural thickening radiology Indeed recently has been hunted by users around us, maybe one of you. People are now accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of this post I will discuss about Nodular Pleural Thickening Radiology.
- Fig 9 2 A B A 65 Year Old Man Diseases Of The Chest Breast Heart And Vessels 2019 2022 Ncbi Bookshelf
- Pleural Thickening Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
- A Systematic Approach To Chest Radiographic Analysis Springerlink
- Pleura Thickening An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
- Benign Pleural Thickening Radiology Key
- Figure 5 Thorax
Find, Read, And Discover Nodular Pleural Thickening Radiology, Such Us:
- Case Of The Month 26 August Ppt Download
- Fig 9 2 A B A 65 Year Old Man Diseases Of The Chest Breast Heart And Vessels 2019 2022 Ncbi Bookshelf
- Pleural Thickening Quibim
- Https Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdfplus 10 2214 Ajr 154 3 2106209
- Pleural Thickening Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
- Mesothelioma Power Plan Workers
- Charles Adams Lawyer
- The Real Erin Brockovich
- Pericardial Mesothelioma Radiology
- Unicorn Traceable Pictures
If you are looking for Unicorn Traceable Pictures you've reached the perfect location. We ve got 104 images about unicorn traceable pictures adding images, photos, photographs, backgrounds, and more. In such page, we additionally have number of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, translucent, etc.
The nodules are 10 15 cm in size and some show central hypodensities.

Unicorn traceable pictures. Blunting of the costophrenic angle is almost always demonstrated. Diffuse pleural thickening may be caused by empyema hemothorax connective tissue disorder or asbestos exposure. Most common causes of nodular pleural thickening are malignant and include.
738 and can progress in size extent and calcification with time. According to etiology it may be classified as. Pleural puncture angle exact value not indicated is depicted as the angle between the outer line of the pleura and the biopsy needle thin arrow.
Metastatic pleural disease particularly from adenocarcinomas eg. November 6 2020 ultrasound guided percutaneous needle biopsy excellent for small pleural lesions diagnosis. Enhanced axial ct c shows nodular pleural thickening arrows.
Nodular pleural thickening is a form of pleural thickening. No lesions are seen in the lungs. Enhanced axial ct c shows nodular pleural thickening arrows.
Plaques typically have edges that are thicker than the central portion fig. No pleural effusion or lymphadenopathy is seen. On ct a pleural plaque is defined as a discontinuous soft tissue focal thickening of the pleural surface with or without foci of calcification.
Diffuse pleural thickening results from an inflammatory pleuritis that fuses the visceral and parietal pleura potentially causing restrictive lung physiology. 84 year old man diagnosed with pleural metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma on us guided pcpnb. Abstract pleural thickening has a variety of causes and often must be distinguished from pleural masses while pleural calcifications are frequently the result of chronic infections including bacterial or tuberculous empyema.
It can occur with both benign and malignant pleural disease. The computed tomogram of the chest fig 4 shows nodular thickening of the left pleura. The nodular thickening extends to the mediastinal pleura.
Pleural thickening is a descriptive term given to describe any form of thickening involving either the parietal or visceral pleura.
More From Unicorn Traceable Pictures
- Pirate Pumpkin Face
- Kel Law Firm
- Mesothelioma Doctors Near Longview Texas
- Pancreatic Cancer And Mesothelioma
- Left Pleural Thickening
Incoming Search Terms:
- 3 The Pleura Left Pleural Thickening,
- Comparative Interpretation Of Ct And Standard Radiography Of The Pleura Left Pleural Thickening,
- Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging Left Pleural Thickening,
- Epos Trade Left Pleural Thickening,
- Nodular Pleural Thickening In A Young Woman The Bmj Left Pleural Thickening,
- Benign Pleural Thickening Radiology Key Left Pleural Thickening,