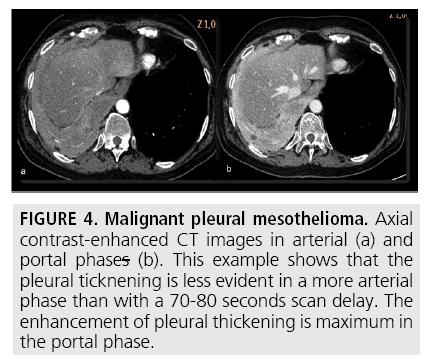
Malignant Pleural Thickening, Https Jksronline Org Synapse Data Pdfdata 1016jkrs Jkrs 26 735 Pdf
Malignant pleural thickening Indeed lately has been sought by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view image and video data for inspiration, and according to the name of this post I will discuss about Malignant Pleural Thickening.
- Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Pulmonology Advisor
- Thorax 8 2 Pleural Space Case 8 2 2 Benign And Malignant Pleural Thickening Ultrasound Cases
- Figure 3 From Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Role Of Ct Mri And Pet Ct In Staging Evaluation And Treatment Considerations Semantic Scholar
- Initial Chest X Ray And Ct Show That Massive Pleural Effusion In The Download Scientific Diagram
- Nodular Pleural Thickening In A Young Woman The Bmj
- Malignant Pleural Effusion Pulmonology Advisor
Find, Read, And Discover Malignant Pleural Thickening, Such Us:
- Pleural Malignant Mesothelioma With Micropapillary Pattern A Case Report And Literature Review
- Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Pulmonology Advisor
- Wk 7 Non Cardiac Chest Thorax 8 2 Pleural Space Case 8 2 2 Benign And Malignant Pleural Thickening Ultrasound Cases Thorax Ultrasound Cardiac
- Diagnostic Value Of Medical Thoracoscopy In Malignant Pleural Effusion Induced By Non Hodgkin S Lymphoma
- Benign Pleural Thickening Radiology Key
- Cute Baby Animal Coloring Pages
- Ice Cream Cone Coloring Page
- Captain Underpants Colouring
- Simple Ice Cream Cone Coloring Page
- Mesothelioma Foundation
If you re searching for Mesothelioma Foundation you've reached the ideal location. We ve got 104 graphics about mesothelioma foundation adding pictures, photos, photographs, wallpapers, and more. In these web page, we additionally provide number of images out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, transparent, etc.
Pleural thickening that is nodular circumferential and greater than 1 cm in thickness is highly suggestive of malignant pleural disease including mpm.
Mesothelioma foundation. The portal venous phase also. In some cases pleural thickening can be benign. Pleural thickening is a descriptive term given to describe any form of thickening involving either the parietal or visceral pleura.
Ct is the work horse of pleural imaging able to achieve specificities of close to 100 3. Diffuse pleural thickening refers to widespread pleural thickening and usually affects the visceral pleura. Malignant pleural thickening has lesion characteristic of irregular nodular opacities on the periphery with or without pleural effuse in chest x ray and in chest ct shows the form.
In cases where multiple nodular regions or pleural thickening are present the diagnosis may be evident especially if a primary tumor or other metastatic deposits are visible. In cases of osseous or cartilaginous differentiation ossification or calcification may be seen in regions of pleural abnormality and the extent may be scattered or diffuse. Focal pleural thickening is a term which can be used to describe a single area of pleural thickening often referred to as pleural plaque.
The histopathology is malignant epitheloid cell forms a cohesive nest glandular structure and a lot of micropapillae in accordance with malignant mesothelioma. Lung cancer and breast cancer account for about 50 65 of malignant pleural effusions. Pleural thickening is a condition triggered by asbestos exposure that causes the pleural lining of the lungs known as the pleura to thicken with scar tissue.
According to etiology it may be classified as. This scarring also known as fibrosis restricts lung function and may cause chest pain and difficulty breathing. It can occur with both benign and malignant pleural disease.
Other common causes include pleural mesothelioma and lymphoma. Mri signal intensity on t2 weighted images differentiates malignant and benign pleural thickening with a level of accuracy similar to that of ct so it may be useful in difficult cases where there is ambiguity about the ct results. Whether malignant or benign pleural thickening cannot be cured.
Malignant pleural effusion is a condition in which cancer causes an abnormal amount of fluid to collect between the thin layers of tissue lining the outside of the lung and the wall of the chest cavity. See malignant vs benign pleural effusion. However benign pleural thickening can impede a patients lung function if the thickening becomes too advanced.
Malignant pleural thickening tends to show inhomogenous hyperintensity on proton density t2 weighted images and enhancement on t1 weighted images following gadolinium injection in contradistinction to benign disease that is of low signal on both sequences.
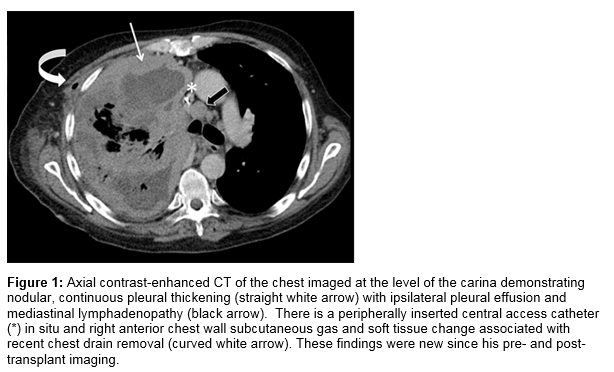
First Reported Finding Of A Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma In A Patient Post Liver Transplant Irish Medical Journal Mesothelioma Foundation
More From Mesothelioma Foundation
- Testicular Mesothelioma Staging
- Vision Law Mesothelioma
- Unicorn Colouring In Picture
- Printable Ghost Pictures
- Sophie Jacoby
Incoming Search Terms:
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcspmwnilmuhk8i39kt69xi5gleiqehe9gtxfhhnhkwwfyfx6syw Usqp Cau Sophie Jacoby,
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gct5wagysvxv6irl7dgfam2 Tlmenkhg96a8naqacd 7ymwnujus Usqp Cau Sophie Jacoby,
- Fishman S Pulmonary Diseases And Disorders Fifth Edition Sophie Jacoby,
- Initial Chest X Ray And Ct Show That Massive Pleural Effusion In The Download Scientific Diagram Sophie Jacoby,
- Types Of Pleural Thickening Pleural Thickening Sophie Jacoby,
- Pdf Pet For The Evaluation Of Pleural Thickening Observed On Ct Semantic Scholar Sophie Jacoby,