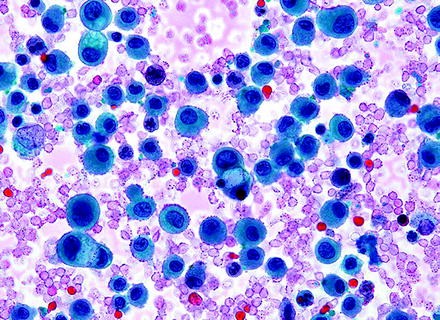
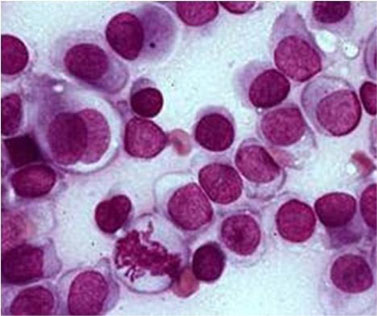
Malignant Mesothelial Cells Cytology, Https Www Rcpath Org Asset Ed8cdd8d 8d04 4b82 Ad48d585e2f023be
Malignant mesothelial cells cytology Indeed lately is being sought by users around us, perhaps one of you. People now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view video and image data for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will talk about about Malignant Mesothelial Cells Cytology.
- Mesothelioma Vs Adenocarcinoma Cytology Creative Art
- A Panel Of Markers For Identification Of Malignant And Non Malignant Cells In Culture From Effusions
- Diagnostic Utility Of The Cell Block Method Versus The Conventional Smear Study In Pleural Fluid Cytology Shivakumarswamy U Arakeri Su Karigowdar Mh Yelikar B R J Cytol
- Pathology Outlines Mesothelioma Epithelioid
- Multiple Myeloma Presenting As Bilateral Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Cytomorphological Profile Of Neoplastic Effusions An Audit Of 10 Years With Emphasis On Uncommonly Encountered Malignancies Gupta S Sodhani P Jain S J Can Res Ther
Find, Read, And Discover Malignant Mesothelial Cells Cytology, Such Us:
- Fluid Cytology In Serous Cavity Effusions
- Https Www Hkiap Org Wp Content Uploads Lecture Notes 2019 20special 20cytology 20workshop Mesothelioma 20how 20far Pdf
- Http Labmed Oxfordjournals Org Content Labmed 29 1 26 Full Pdf
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcseb7aizju0qbedevvi8irefmeqt7 Rh3pa 8irkz1p4jn0mu35 Usqp Cau
- Effusion Cytology Diagnosis
- What Are Asbestos Fibers
- Printable Rudolph Coloring Pages
- Tractor Coloring Pages For Boys
- Corporate Securities Law
- Law Offices Of Joe Bornstein
If you re looking for Law Offices Of Joe Bornstein you've reached the ideal location. We ve got 104 graphics about law offices of joe bornstein adding images, pictures, photos, wallpapers, and more. In such web page, we additionally have number of graphics out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, logo, blackandwhite, transparent, etc.
Focal macronucleoli are seen in reactive mesothelial cells.

Law offices of joe bornstein. Bap1 immunohistochemical ihc staining of malignant mesothelioma mm and reactive mesothelial cell rmc proliferations in cytology samples. Nuclear membrane irregularies rare. The use of immunohistochemistry to distinguish reactive mesothelial cells from malignant mesothelioma in cytologic effusions.
Note internal control of rmcs and histiocytes. The differential diagnosis between reactive mesothelial cells rms malignant mesotheliomas mms and adenocarcinomas acs is often difficult in cytologic specimens and the utility of various immunohistochemical markers have been explored. The most commonly cited feature useful in making a diagnosis was architectural atypia in the form of large groups of mesothelial cells with knobby borders.
Mpm is usually a difficult tumor to diagnose and to differentiate both from other tumors involving the pleura and particularly from benign pleural proliferations. The histologic examination of pleural tissues together with the presence of stromal or fat invasion is then required to differentiate malignant from benign pleural lesions. B absence of nuclear bap1 ihc staining for in malignant cells.
10 cells in a cluster rare in benign. 3 6 first clinical symptoms including pleural effusions 7 are not specific. In this study we describe a computational method to detect malignant mesothelioma based on the nuclear chromatin distribution from digital images of mesothelial cells in effusion cytology specimens.
Clusters of cells with knobby border. Examination of nuclear chromatin distribution of the mesothelial cells to determine the presence of mesothelioma is a challenging task for cytopathologists because benign and malignant nuclei look similar to human eye. Glut 1 ema and desmin expression were evaluated by immunocytochemistry on cbs.
The two lectures and the afternoon workshop session review the literature describe the cytomorphological criteria in the diagnosis of reactiveproliferative mesothelial cells inflammatory infectious conditions and neoplastic lesions in body fluid with emphasis on the many faces and similarities of reactive mesothelial cells and malignant cells. Forty three effusion cytology cbs of 25 confirmed malignant mesotheliomas were compared to cbs of 23 benign mesothelial effusions without inflammation and 13 reactive mesothelial proliferations associated with inflammation. The next most commonly cited features were high cellularity in effusions composed of mesothelial cells and effusions containing mesothelial cells with marked cytologic atypia.
A mm epithelioid type he 40x objective. Large clusters of cells. C mm papillary type.
A reappraisal and results of a multi institution survey.
More From Law Offices Of Joe Bornstein
- Scarecrow Coloring Page For Kids
- Mesothelioma Lawyer Indianapolis
- Office Lawers
- Hot Halloween Costume Ideas
- Disney Pixar Coloring Pages
Incoming Search Terms:
- A Panel Of Markers For Identification Of Malignant And Non Malignant Cells In Culture From Effusions Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,
- Effusions Cytopathology Cellnetpathology Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,
- Sheet Of Reactive Mesothelial Cells Note Owindowso Between Cells And Download Scientific Diagram Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,
- Home Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,
- Https Www Hkiap Org Wp Content Uploads Lecture Notes 2019 20special 20cytology 20workshop Mesothelioma 20how 20far Pdf Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,
- Shutterstock Puzzlepix Disney Pixar Coloring Pages,