Pleural Fluid Of Patient With Pulmonary Mesothelioma, Recommendations For The Diagnosis And Management Of Asbestos Related Pleural And Pulmonary Disease Archivos De Bronconeumologia English Edition
Pleural fluid of patient with pulmonary mesothelioma Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you. Individuals are now accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the title of the article I will discuss about Pleural Fluid Of Patient With Pulmonary Mesothelioma.
- Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Scandinavian Journal Of Work Environment Health Asbestos Asbestosis And Cancer The Helsinki Criteria For Diagnosis And
- Pleural Mesothelioma Dr Tinku Joseph
- Diagnostic Value Of Immunopathology In Malignant Pleural Tumors Farag Ts Farag As Oreiby Ha Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc
- Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html
- Secretome Of Pleural Effusions Associated With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Nsclc And Malignant Meso Eurekalert Science News
Find, Read, And Discover Pleural Fluid Of Patient With Pulmonary Mesothelioma, Such Us:
- Pleural Effusion Biomarkers And Computed Tomography Findings In Diagnosing Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma A Retrospective Study In A Single Center
- Malignant Pleural Effusion And Incidence Of Pleural Thickening In Thorax Ct European Respiratory Society
- Pleural Effusion In Adults Etiology Diagnosis And Treatment 24 05 2019
- Diagnosis And Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions State Of The Art In 2017 Desai Journal Of Thoracic Disease
- Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Mesothelioma Maintanece Chemo
- Wednesday Costume
- Unicorn Coloring Sheets
- Lol Colouring Pages Free
- Williams Associates Law Firm
If you are looking for Williams Associates Law Firm you've come to the right location. We have 100 graphics about williams associates law firm including images, photos, photographs, backgrounds, and much more. In such page, we additionally provide variety of graphics out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, transparent, etc.
Aggressive Drainage Regimen May Promote Spontaneous Pleurodesis Chest Physician Williams Associates Law Firm
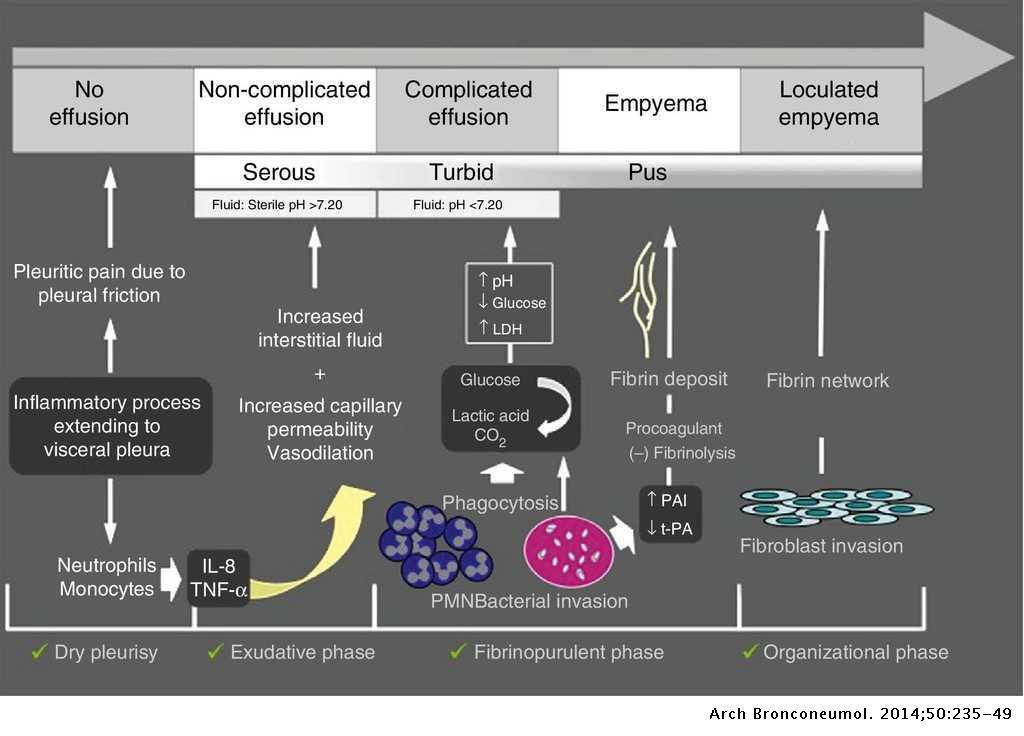
Recommendations Of Diagnosis And Treatment Of Pleural Effusion Update Archivos De Bronconeumologia English Edition Williams Associates Law Firm
Pleural fluid glucose correlates with ph and has similar clinical implications.

Williams associates law firm. Luckily doctors have several minimally invasive options for removing this fluid to help mesothelioma patients breathe easier. Lievense la1 cornelissen r2 bezemer k2 kaijen lambers me2 hegmans jp2 aerts jg3. Although patients with a low pleural fluid ph ph73 are more likely to have a poorer overall survival and unsuccessful pleurodesis its predictive accuracy is poor and should not be used to guide patient care.
Other symptoms felt by patients with pleural mesothelioma. Pleural effusions are a common diagnosis in the united states and generally indicate a larger condition or disease. Pleural fluid characteristics of 26 patients diagnosed with malignant mesothelioma over an 18 year period were reviewed and compared with those of patients with effusions due to other malignancies.
While a pleural effusion may be a symptom of pleural mesothelioma itself the condition can also cause its own symptoms like breathlessness. 1department of pulmonary medicine erasmus medical center cancer institute rotterdam the netherlands. Pleural effusion of patients with malignant mesothelioma induces macrophage mediated t cell suppression.
Most pleural mesothelioma patients experience pleural effusion the buildup of fluid in the pleural space around the lungs. It is a typical complication of pleural mesothelioma and is uncomfortable or even painful. This fluid can cause pain for patients by restricting the lungs from expanding normally.
A pleural effusion is a buildup of excess fluid between the lining of the lungs and chest cavity. Pleural effusion can be treated to relieve patients symptoms. Treatment involves draining the fluid but if it continues to accumulate more permanent procedures may be required.
This excess can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs. Pleural effusion may be a symptom of mesothelioma lung cancer or other diseases. A 2019 study of 229 patients with mesothelioma found 83 had a pleural effusion at presentation and nonexpandable lung was observed in 33 of this group.
Pleural effusions may signal a developing asbestos related disease such as pleural thickening and contribute to its progression. For pleural mesothelioma patients pleural effusions develop in the majority of cases especially among patients with late stage disease. Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates in the pleural cavity the fluid filled space that surrounds the lungs.
Primarily affecting the respiratory system pleural mesothelioma symptoms impact the airways lungs and breathing muscles. Survival from time of initial thoracentesis was directly correlated with pleural ph and decreased pleural fluidserum glucose ratios but was not. Pleural fluid ph is often low in mesothelioma.
Caused by excess fluids pleural effusion in the lining of the lungs some of the first signs a patient may feel are a persistent cough and shortness of breath.

Comparison Of Additional Diagnostic Values Of Pleural Fluid Cytology Download Table Williams Associates Law Firm
More From Williams Associates Law Firm
- Free Nativity Coloring Pages
- June Coloring Pages
- Realistic Elephant Pictures To Color
- Kevin Blyth Mesothelioma
- Ros 10
Incoming Search Terms:
- Scandinavian Journal Of Work Environment Health Asbestos Asbestosis And Cancer The Helsinki Criteria For Diagnosis And Ros 10,
- Pdf Concentration Of Hyaluronic Acid In Pleural Fluid As A Diagnostic Aid For Malignant Mesothelioma Semantic Scholar Ros 10,
- Diagnosis In Patients With Pleural Effusions Download Table Ros 10,
- Diagnostic Yield Of Pleural Fluid Cytology In Malignant Effusions An Australian Tertiary Centre Experience Loveland 2018 Internal Medicine Journal Wiley Online Library Ros 10,
- Pleural Irregularities And Mediastinal Pleural Involvement In Early Stages Of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma And Benign Asbestos Pleural Effusion European Journal Of Radiology Ros 10,
- Secretome Of Pleural Effusions Associated With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Nsclc And Malignant Meso Eurekalert Science News Ros 10,