Causes Of Pleural Thickening Radiology, Chest X Ray One Year Later Mild Pleural Thickening And Linear Download Scientific Diagram
Causes of pleural thickening radiology Indeed recently has been sought by users around us, perhaps one of you personally. Individuals now are accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of the article I will discuss about Causes Of Pleural Thickening Radiology.
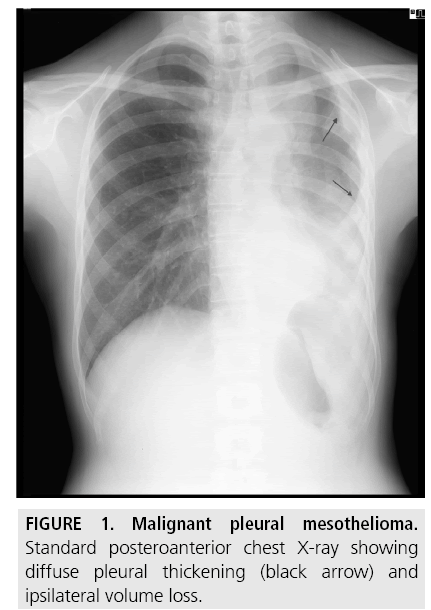
- View Of Malignant Mesothelioma The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles
- Pdf Pleural Disease In Silicosis Pleural Thickening Effusion And Invagination1
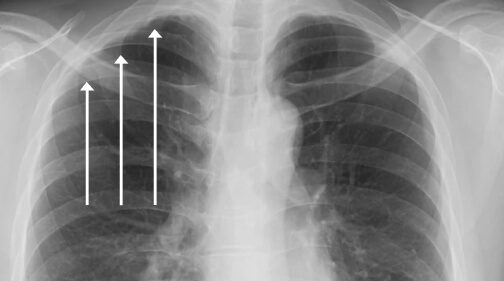
- Pleural Thickening In The Apices
- Pleural Thickening Symptoms Causes And Treatment
- Diagnostic Imaging And Workup Of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- Fibrothorax Wikipedia
Find, Read, And Discover Causes Of Pleural Thickening Radiology, Such Us:
- Investigating Pleural Thickening The Bmj
- Radiological Review Of Pleural Tumors Sureka B Thukral Bb Mittal Mk Mittal A Sinha M Indian J Radiol Imaging
- Pleural Thickening Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
- Https Www Chestmed Theclinics Com Article S0272 5231 06 00037 2 Pdf
- Imaging Of The Pleura Helm 2010 Journal Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Wiley Online Library
- Meyers Leonard Wife
- Claim Assistance For Mesothelioma Veterans
- Financial Assistance And Compensation For Mesothelioma
- Halloween Decorations 2019
- Early Symptoms Of Asbestos Exposure
If you are looking for Early Symptoms Of Asbestos Exposure you've come to the right place. We have 104 graphics about early symptoms of asbestos exposure adding images, photos, pictures, wallpapers, and much more. In such web page, we additionally have variety of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, translucent, etc.

Frontal Chest Radiograph Shows Bilateral Calcified Pleural Thickening There Is A Subtle Increase In Density Of The Central Inferi Radiology Radiographer Chest Early Symptoms Of Asbestos Exposure
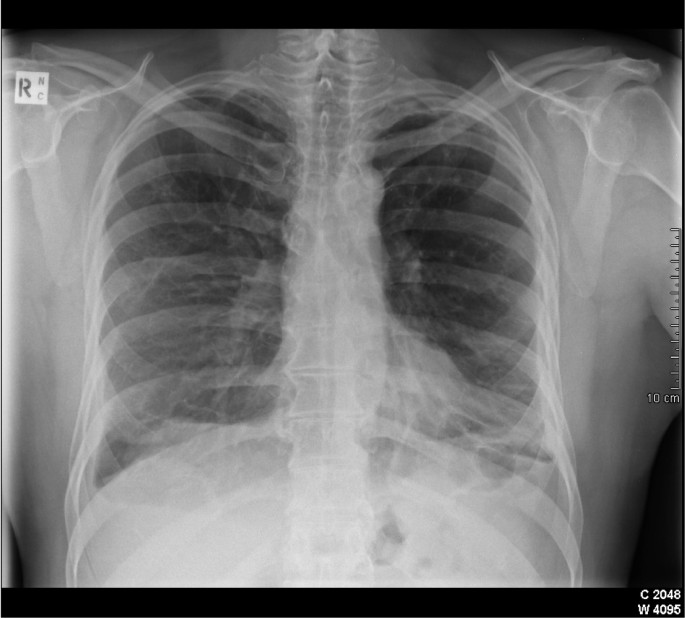
The principal consideration is a malignant pleural tumor.

Early symptoms of asbestos exposure. According to etiology it may be classified as. Infection involving the pleura. The pleural plaques of asbestos may be localized soft tissue but frequently calcify with a characteristic radiologic appearance on both chest x ray and ct.
Pathology etiology most common causes of nodular pleural thickening are malignant and include. Apical pleural cap refers to a curved density at the lung apex seen on chest radiograph. It can occur with both benign and malignant pleural disease.
Nodular pleural thickening is a form of pleural thickening. Metastatic pleural disease particularly from adenocarcinomas eg. Pleural effusions are usually unilateral and may be loculated fig 6.
Pleural thickening is a condition triggered by asbestos exposure that causes the pleural lining of the lungs known as the pleura to thicken with scar tissue. The pleura show a variety of patterns of fibrosis. Calcified pleural plaques from asbestos exposure.
Pleural calcification can be the result of a wide range of pathology and can be mimicked by a number of conditionsartifacts. The frequency of apical pleural thickening increases with age 3. Pleural fibrosis has a number of causes and is the outcome of many pleural diseases and a potential complication of every inflammatory condition that affects the lungs.
Pleural thickening is the next most common finding and is seen more often than pleural effusion. Abstract pleural thickening has a variety of causes and often must be distinguished from pleural masses while pleural calcifications are frequently the result of chronic infections including bacterial or tuberculous empyema. Secondary to previous apical infection.
Pyothoraxempyema tuberculous pleuritis 3. Asbestos related pleural disease. Diffuse pleural thickening refers to a morphological type of pleural thickening.
It arises from a number of causes. It can occur from malignant as well as nonmalignant causes which include. They usually occur late in the disease and are commonly associated with pericarditis and subcutaneous nodules.
Malignant pleural tumor causes nodular and asymmetric pleural thickening 1 cm that may involve both the mediastinal and lateral pleural compartments 12. This scarring also known as fibrosis restricts lung function and may cause chest pain and difficulty breathing. Diffuse pleural fibrosis fibrothorax 6.
Typically seen a continuous sheet of pleural thickening often involving the costophrenic angles and apices without calcification 2 3. Pleural thickening is a descriptive term given to describe any form of thickening involving either the parietal or visceral pleura. Benign pleural thickening caused by fibrosis is the second most common pleural abnormality the most common one being effusion.
More From Early Symptoms Of Asbestos Exposure
- Law Os Sines
- Sarcomatoid Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Happy Halloween Dog Images
- Mesothelioma One Time Exposure Asbestos
- Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers
Incoming Search Terms:
- Https Www Resmedjournal Com Article S0954 6111 17 30033 1 Pdf Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,
- Imaging Of The Pleura Helm 2010 Journal Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Wiley Online Library Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,
- Pleural Thickening On Screening Chest X Rays A Single Institutional Study Respiratory Research Full Text Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,
- Pleura Chest Wall And Diaphragm Chest Radiology The Essentials 2nd Edition Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,
- 2 Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,
- Radiology Corner European Respiratory Society Monessen Mesothelioma Lawyers,